Elapsed Time = 0 Hours
Max Altitude = 0 km
Max Altitude = 0 km
Enter a satellite's initial altitude and velocity to trace its orbital path around the Earth. The orbital path is to scale relative to the size of the Earth. Gravity is assumed to be the only force acting on the satellite, where
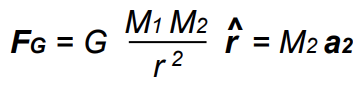
Use the thrusters to increase or decrease the satellite's velocity by 5 % and move it into different orbits.
For reference, the International Space Station orbits at ~ 405 km above the surface at an average velocity of 7.66 km/s.
Geosynchronous satellites orbit at an altitude of 35,786 km above the surface at a speed of 3.075 km/s.
Elapsed Time = 0 Hours
Max Altitude = 0 km
Min Altitude = 0 km